Do Courses, Content Mills, Joc/gil Drawing, Speechpad

Reinforcement Q-Learning from Scratch in Python with OpenAI Gym
Teach a Taxi to pick up and drib off passengers at the right locations with Reinforcement Learning
Near of you have probably heard of AI learning to play computer games on their own, a very popular instance being Deepmind. Deepmind hit the news when their AlphaGo programme defeated the S Korean Go globe champion in 2016. There had been many successful attempts in the past to develop agents with the intent of playing Atari games similar Breakout, Pong, and Space Invaders.
Each of these programs follow a paradigm of Machine Learning known every bit Reinforcement Learning. If you lot've never been exposed to reinforcement learning before, the following is a very straightforward illustration for how information technology works.
Y'all will larn:
- What Reinforcement Learning is and how it works
- How to work with OpenAI Gym
- How to implement Q-Learning in Python
Consider the scenario of instruction a dog new tricks. The dog doesn't understand our linguistic communication, so we can't tell him what to do. Instead, we follow a different strategy. We emulate a situation (or a cue), and the domestic dog tries to respond in many dissimilar means. If the domestic dog'south response is the desired one, we reward them with snacks. Now approximate what, the adjacent time the canis familiaris is exposed to the same situation, the dog executes a similar action with even more enthusiasm in expectation of more food. That's like learning "what to practice" from positive experiences. Similarly, dogs will tend to acquire what not to do when face with negative experiences.
That's exactly how Reinforcement Learning works in a broader sense:
- Your canis familiaris is an "agent" that is exposed to the environment. The environment could in your business firm, with y'all.
- The situations they encounter are coordinating to a state. An example of a state could exist your dog continuing and yous use a specific discussion in a sure tone in your living room
- Our agents react by performing an action to transition from one "land" to another "country," your dog goes from standing to sitting, for example.
- After the transition, they may receive a advantage or punishment in return. You give them a treat! Or a "No" as a penalization.
- The policy is the strategy of choosing an activeness given a state in expectation of better outcomes.
Reinforcement Learning lies between the spectrum of Supervised Learning and Unsupervised Learning, and there's a few of import things to note:
- Being greedy doesn't always work
There are things that are piece of cake to do for instant gratification, and at that place'southward things that provide long term rewards The goal is to not be greedy by looking for the quick immediate rewards, but instead to optimize for maximum rewards over the whole training.
- Sequence matters in Reinforcement Learning
The reward amanuensis does non just depend on the current state, simply the entire history of states. Different supervised and unsupervised learning, fourth dimension is important hither.
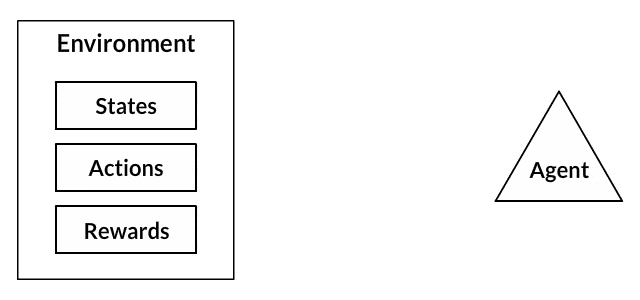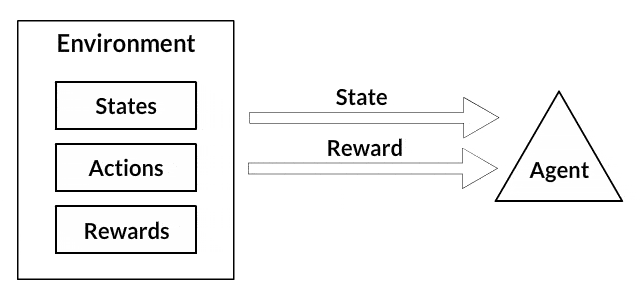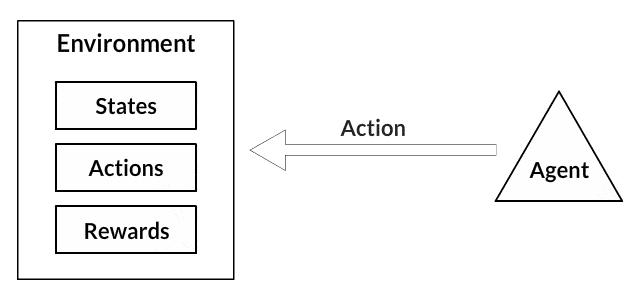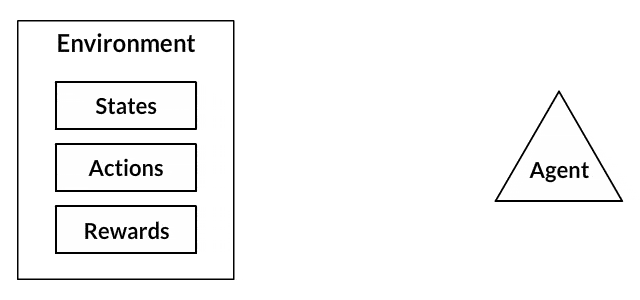
In a way, Reinforcement Learning is the science of making optimal decisions using experiences. Breaking it downward, the process of Reinforcement Learning involves these simple steps:
- Observation of the environment
- Deciding how to deed using some strategy
- Interim accordingly
- Receiving a advantage or penalization
- Learning from the experiences and refining our strategy
- Iterate until an optimal strategy is plant
Let's now empathize Reinforcement Learning by really developing an agent to learn to play a game automatically on its ain.
Let'south pattern a simulation of a cocky-driving cab. The major goal is to demonstrate, in a simplified surroundings, how you tin use RL techniques to develop an efficient and condom approach for tackling this problem.
The Smartcab'due south task is to pick up the passenger at one location and drop them off in another. Here are a few things that nosotros'd honey our Smartcab to take intendance of:
- Drop off the rider to the right location.
- Save passenger'southward fourth dimension by taking minimum fourth dimension possible to drib off
- Take intendance of passenger's safety and traffic rules
There are different aspects that need to exist considered hither while modeling an RL solution to this problem: rewards, states, and actions.
Since the agent (the imaginary commuter) is advantage-motivated and is going to learn how to control the cab past trial experiences in the environment, we need to determine the rewards and/or penalties and their magnitude appropriately. Here a few points to consider:
- The agent should receive a high positive reward for a successful dropoff because this behavior is highly desired
- The agent should exist penalized if it tries to drop off a passenger in wrong locations
- The amanuensis should get a slight negative reward for non making it to the destination after every time-step. "Slight" negative because nosotros would prefer our agent to attain late instead of making wrong moves trying to reach to the destination as fast every bit possible
In Reinforcement Learning, the amanuensis encounters a land, and then takes action co-ordinate to the state it's in.
The Country Space is the prepare of all possible situations our taxi could inhabit. The land should incorporate useful data the amanuensis needs to make the right action.
Let's say we have a training expanse for our Smartcab where we are teaching it to transport people in a parking lot to four dissimilar locations (R, G, Y, B):

Let'due south assume Smartcab is the only vehicle in this parking lot. We tin break upwardly the parking lot into a 5x5 grid, which gives u.s.a. 25 possible taxi locations. These 25 locations are one office of our country space. Observe the electric current location state of our taxi is coordinate (three, i).
You'll also notice in that location are iv (4) locations that nosotros can selection upward and drib off a passenger: R, G, Y, B or [(0,0), (0,4), (4,0), (iv,3)] in (row, col) coordinates. Our illustrated passenger is in location Y and they wish to go to location R.
When we besides account for one (ane) additional passenger country of being inside the taxi, we can take all combinations of rider locations and destination locations to come to a total number of states for our taxi surroundings; there'due south four (iv) destinations and 5 (four + one) passenger locations.
And then, our taxi environment has $5 \times 5 \times 5 \times four = 500$ full possible states.
The amanuensis encounters i of the 500 states and it takes an action. The action in our example can be to move in a direction or decide to pickup/dropoff a passenger.
In other words, we have vi possible deportment:
-
due south -
north -
east -
due west -
pickup -
dropoff
This is the action space: the set of all the deportment that our amanuensis can accept in a given state.
You'll observe in the illustration above, that the taxi cannot perform certain actions in certain states due to walls. In environment'south code, we will simply provide a -1 punishment for every wall hit and the taxi won't move anywhere. This volition just rack up penalties causing the taxi to consider going around the wall.
Fortunately, OpenAI Gym has this verbal surround already built for u.s..
Gym provides different game environments which nosotros can plug into our lawmaking and test an agent. The library takes care of API for providing all the information that our agent would require, like possible actions, score, and current state. We just need to focus only on the algorithm part for our agent.
We'll be using the Gym environment chosen Taxi-V2, which all of the details explained higher up were pulled from. The objectives, rewards, and actions are all the same.
Nosotros need to install gym outset. Executing the post-obit in a Jupyter notebook should work:
One time installed, we tin can load the game surround and render what it looks like:
+---------+ |R: | : :K| | : : : : | | : : : : | | | : | : | |Y| : |B: | +---------+
The core gym interface is env, which is the unified environment interface. The following are the env methods that would exist quite helpful to united states of america:
-
env.reset: Resets the surroundings and returns a random initial country. -
env.step(action): Step the environment by one timestep. Returns- observation: Observations of the environment
- reward: If your action was beneficial or non
- washed: Indicates if nosotros accept successfully picked up and dropped off a rider, also called one episode
- info: Boosted info such every bit performance and latency for debugging purposes
-
env.render: Renders one frame of the surroundings (helpful in visualizing the surroundings)
Notation: We are using the .env on the finish of brand to avoid training stopping at 200 iterations, which is the default for the new version of Gym (reference).
Here's our restructured trouble statement (from Gym docs):
"At that place are 4 locations (labeled by different messages), and our job is to choice up the rider at i location and driblet him off at another. We receive +20 points for a successful drop-off and lose 1 point for every time-step it takes. There is also a 10 point penalty for illegal pick-up and drop-off actions."
Let's dive more into the surround.
+---------+ |R: | : :1000| | : : : : | | : : : : | | | : | : | |Y| : |B: | +---------+ Activity Space Discrete(six) State Space Discrete(500)
- The filled square represents the taxi, which is xanthous without a passenger and light-green with a passenger.
- The pipe ("|") represents a wall which the taxi cannot cross.
- R, G, Y, B are the possible pickup and destination locations. The blue letter represents the electric current passenger pick-up location, and the imperial letter is the electric current destination.
As verified past the prints, we accept an Activity Space of size six and a State Space of size 500. As you'll see, our RL algorithm won't need whatever more information than these two things. All nosotros need is a way to identify a state uniquely by assigning a unique number to every possible state, and RL learns to choose an action number from 0-5 where:
- 0 = south
- i = due north
- ii = east
- iii = due west
- 4 = pickup
- 5 = dropoff
Call back that the 500 states correspond to a encoding of the taxi's location, the passenger's location, and the destination location.
Reinforcement Learning will learn a mapping of states to the optimal action to perform in that country by exploration, i.east. the agent explores the environment and takes actions based off rewards divers in the environment.
The optimal action for each state is the action that has the highest cumulative long-term reward.
We can actually take our illustration above, encode its state, and give it to the surround to return in Gym. Recollect that we take the taxi at row 3, column 1, our passenger is at location 2, and our destination is location 0. Using the Taxi-v2 land encoding method, nosotros can exercise the following:
State: 328 +---------+ |R: | : :G| | : : : : | | : : : : | | | : | : | |Y| : |B: | +---------+
We are using our illustration's coordinates to generate a number corresponding to a state betwixt 0 and 499, which turns out to exist 328 for our illustration's state.
Then we can prepare the environs'south country manually with env.env.south using that encoded number. You can play around with the numbers and you'll see the taxi, passenger, and destination move around.
When the Taxi environment is created, there is an initial Reward table that'south as well created, chosen `P`. We can recollect of information technology like a matrix that has the number of states as rows and number of actions equally columns, i.e. a $states \ \times \ actions$ matrix.
Since every state is in this matrix, we can see the default reward values assigned to our illustration'due south state:
This dictionary has the structure {action: [(probability, nextstate, reward, done)]}.
A few things to note:
- The 0-v corresponds to the actions (southward, north, east, due west, pickup, dropoff) the taxi can perform at our electric current state in the analogy.
- In this env,
probabilityis always 1.0. - The
nextstateis the state we would exist in if we take the activeness at this alphabetize of the dict - All the motion actions have a -1 advantage and the pickup/dropoff deportment have -10 advantage in this particular state. If we are in a state where the taxi has a passenger and is on top of the right destination, we would see a reward of xx at the dropoff action (v)
-
doneis used to tell us when we have successfully dropped off a rider in the correct location. Each successfull dropoff is the end of an episode
Note that if our amanuensis chose to explore action two (2) in this land it would be going East into a wall. The source code has made it impossible to really movement the taxi beyond a wall, so if the taxi chooses that action, information technology will just keep accruing -1 penalties, which affects the long-term reward.
Allow's see what would happen if we endeavour to animate being-force our way to solving the problem without RL.
Since we take our P table for default rewards in each state, we tin try to have our taxi navigate but using that.
Nosotros'll create an infinite loop which runs until 1 passenger reaches 1 destination (one episode), or in other words, when the received advantage is xx. The env.action_space.sample() method automatically selects one random action from set of all possible actions.
Let's encounter what happens:
Not practiced. Our agent takes thousands of timesteps and makes lots of wrong drop offs to deliver just one rider to the right destination.
This is because nosotros aren't learning from past experience. Nosotros can run this over and over, and it will never optimize. The amanuensis has no memory of which action was best for each state, which is exactly what Reinforcement Learning will practise for us.
We are going to utilise a uncomplicated RL algorithm called Q-learning which will give our amanuensis some memory.
Essentially, Q-learning lets the agent use the environment's rewards to learn, over time, the best action to take in a given country.
In our Taxi environment, we have the reward tabular array, P, that the agent volition learn from. It does thing by looking receiving a reward for taking an action in the electric current country, then updating a Q-value to retrieve if that activeness was beneficial.
The values store in the Q-table are called a Q-values, and they map to a (country, action) combination.
A Q-value for a particular state-action combination is representative of the "quality" of an action taken from that state. Improve Q-values imply meliorate chances of getting greater rewards.
For example, if the taxi is faced with a state that includes a passenger at its current location, information technology is highly likely that the Q-value for pickup is higher when compared to other deportment, like dropoff or north.
Q-values are initialized to an arbitrary value, and every bit the agent exposes itself to the environment and receives dissimilar rewards past executing different actions, the Q-values are updated using the equation:
$$Q({\small state}, {\pocket-sized action}) \leftarrow (1 - \alpha) Q({\small state}, {\small action}) + \alpha \Large({\small advantage} + \gamma \max_{a} Q({\small next \ state}, {\small all \ actions})\Big)$$
Where:
- $\Large \alpha$ (alpha) is the learning rate ($0 < \alpha \leq ane$) - But like in supervised learning settings, $\alpha$ is the extent to which our Q-values are being updated in every iteration.
- $\Big \gamma$ (gamma) is the discount factor ($0 \leq \gamma \leq 1$) - determines how much importance we want to give to future rewards. A loftier value for the discount factor (close to i) captures the long-term constructive accolade, whereas, a discount factor of 0 makes our amanuensis consider only firsthand advantage, hence making it greedy.
What is this saying?
We are assigning ($\leftarrow$), or updating, the Q-value of the amanuensis's current state and action past first taking a weight ($1-\blastoff$) of the old Q-value, then calculation the learned value. The learned value is a combination of the reward for taking the current action in the current state, and the discounted maximum reward from the next state we will be in once we take the electric current activeness.
Basically, nosotros are learning the proper action to have in the current country by looking at the reward for the current country/activeness combo, and the max rewards for the adjacent country. This volition eventually crusade our taxi to consider the route with the best rewards strung together.
The Q-value of a country-action pair is the sum of the instant reward and the discounted future reward (of the resulting state). The way we shop the Q-values for each state and activity is through a Q-table
The Q-table is a matrix where we have a row for every state (500) and a column for every action (6). It's outset initialized to 0, and then values are updated after training. Note that the Q-table has the same dimensions as the reward table, just it has a completely unlike purpose.

Breaking it down into steps, we get
- Initialize the Q-table by all zeros.
- Start exploring actions: For each state, select any 1 among all possible deportment for the current state (S).
- Travel to the next land (S') every bit a effect of that action (a).
- For all possible actions from the state (S') select the one with the highest Q-value.
- Update Q-table values using the equation.
- Set the side by side state as the current land.
- If goal state is reached, then finish and repeat the process.
After plenty random exploration of deportment, the Q-values tend to converge serving our agent equally an action-value function which information technology can exploit to pick the near optimal action from a given state.
There'southward a tradeoff between exploration (choosing a random activity) and exploitation (choosing actions based on already learned Q-values). We want to forbid the action from always taking the same route, and perhaps overfitting, so we'll be introducing another parameter called $\Large \epsilon$ "epsilon" to cater to this during training.
Instead of only selecting the best learned Q-value action, we'll sometimes favor exploring the activity space further. Lower epsilon value results in episodes with more penalties (on average) which is obvious considering we are exploring and making random decisions.
First, nosotros'll initialize the Q-table to a $500 \times half-dozen$ matrix of zeros:
Nosotros tin now create the training algorithm that will update this Q-table as the agent explores the environment over thousands of episodes.
In the showtime office of while not done, we decide whether to pick a random action or to exploit the already computed Q-values. This is done simply by using the epsilon value and comparison information technology to the random.uniform(0, 1) part, which returns an arbitrary number betwixt 0 and ane.
Nosotros execute the chosen action in the environment to obtain the next_state and the advantage from performing the activeness. After that, we calculate the maximum Q-value for the actions corresponding to the next_state, and with that, we can easily update our Q-value to the new_q_value:
Now that the Q-table has been established over 100,000 episodes, permit's run across what the Q-values are at our illustration'due south state:
The max Q-value is "north" (-one.971), then it looks like Q-learning has effectively learned the all-time action to have in our illustration'due south state!
Let'due south evaluate the performance of our agent. Nosotros don't need to explore actions any further, so at present the next activity is always selected using the best Q-value:
Nosotros can see from the evaluation, the agent'due south performance improved significantly and it incurred no penalties, which ways information technology performed the right pickup/dropoff actions with 100 different passengers.
With Q-learning agent commits errors initially during exploration but in one case it has explored enough (seen virtually of u.s.a.), information technology can act wisely maximizing the rewards making smart moves. Let's meet how much better our Q-learning solution is when compared to the agent making merely random moves.
We evaluate our agents according to the following metrics,
- Average number of penalties per episode: The smaller the number, the ameliorate the functioning of our agent. Ideally, nosotros would like this metric to be zip or very close to zero.
- Boilerplate number of timesteps per trip: Nosotros want a pocket-sized number of timesteps per episode as well since we desire our amanuensis to take minimum steps(i.east. the shortest path) to achieve the destination.
- Boilerplate rewards per move: The larger the reward means the agent is doing the correct matter. That's why deciding rewards is a crucial office of Reinforcement Learning. In our instance, as both timesteps and penalties are negatively rewarded, a higher average reward would hateful that the agent reaches the destination every bit fast equally possible with the least penalties"
These metrics were computed over 100 episodes. And every bit the results show, our Q-learning agent nailed it!
The values of `blastoff`, `gamma`, and `epsilon` were by and large based on intuition and some "hit and trial", merely there are amend means to come up upward with good values.
Ideally, all 3 should decrease over time because equally the agent continues to learn, information technology actually builds up more resilient priors;
- $\Large \blastoff$: (the learning charge per unit) should decrease as you go on to gain a larger and larger knowledge base of operations.
- $\Large \gamma$: as you get closer and closer to the borderline, your preference for near-term reward should increment, as you won't be effectually long enough to get the long-term reward, which ways your gamma should decrease.
- $\Large \epsilon$: as nosotros develop our strategy, we have less need of exploration and more exploitation to become more utility from our policy, so equally trials increase, epsilon should decrease.
A elementary way to programmatically come up with the best set of values of the hyperparameter is to create a comprehensive search role (similar to grid search) that selects the parameters that would consequence in all-time reward/time_steps ratio. The reason for reward/time_steps is that nosotros desire to choose parameters which enable united states to get the maximum reward equally fast as possible. We may want to runway the number of penalties corresponding to the hyperparameter value combination as well considering this can likewise exist a deciding factor (we don't want our smart amanuensis to violate rules at the cost of reaching faster). A more fancy way to get the correct combination of hyperparameter values would be to utilize Genetic Algorithms.
Alright! We began with agreement Reinforcement Learning with the help of real-world analogies. We and so dived into the basics of Reinforcement Learning and framed a Self-driving cab as a Reinforcement Learning trouble. We then used OpenAI'southward Gym in python to provide the states with a related environs, where we tin develop our agent and evaluate it. And so we observed how terrible our amanuensis was without using whatsoever algorithm to play the game, so we went ahead to implement the Q-learning algorithm from scratch. The amanuensis's performance improved significantly after Q-learning. Finally, we discussed better approaches for deciding the hyperparameters for our algorithm.
Q-learning is 1 of the easiest Reinforcement Learning algorithms. The problem with Q-learning however is, once the number of states in the environment are very high, it becomes difficult to implement them with Q table as the size would get very, very large. State of the art techniques uses Deep neural networks instead of the Q-table (Deep Reinforcement Learning). The neural network takes in state information and actions to the input layer and learns to output the right action over the time. Deep learning techniques (like Convolutional Neural Networks) are also used to interpret the pixels on the screen and excerpt information out of the game (like scores), and then letting the agent control the game.
We have discussed a lot about Reinforcement Learning and games. But Reinforcement learning is not just limited to games. Information technology is used for managing stock portfolios and finances, for making humanoid robots, for manufacturing and inventory management, to develop general AI agents, which are agents that can perform multiple things with a unmarried algorithm, like the same agent playing multiple Atari games. Open AI too has a platform called universe for measuring and training an AI's full general intelligence across myriads of games, websites and other general applications.
If you'd similar to continue with this project to make it better, hither'south a few things you can add:
- Plow this code into a module of functions that can apply multiple environments
- Melody alpha, gamma, and/or epsilon using a decay over episodes
- Implement a grid search to find the best hyperparameters
Shoot usa a tweet @learndatasci with a repo or gist and we'll check out your additions!
Source: https://www.learndatasci.com/tutorials/reinforcement-q-learning-scratch-python-openai-gym/
Posted by: ellisphyan1939.blogspot.com


0 Response to "Do Courses, Content Mills, Joc/gil Drawing, Speechpad"
Post a Comment